In Japanese this is pronounced "kaizen"
改 ("kai") means "change" or "the action to correct".
善 ("zen") means "good".
In Korean this is pronounced "ge sun"
改善 ("ge sun") means "improvement" or "change for the better"
In Chinese this is pronounced "gai shan":
改善 ("gǎi shàn") means "change for the better" or "improve".
改 ("gǎi") means "change" or "the action to correct".
善 ("shàn") means "good" or "benefit".
Kaizen means simply "improvement" in Japanese. Kaizen strategy calls for never-ending efforts for improvement involving everyone in the organization. When used inside an organization properly, everyone from the CEO to the janitor, even external stakeholders can participate in the continuous improvement.
A main difference culturally is in the western continents, such as USA, Americans are very motivated by monetary gains when it comes to achievements. In the east it is much different. Involvement in something bigger, making a difference, and being noticed for achievements is more meaningful. For instance many companies incorporate kaizen very purposely.
Quick and Easy Kaizen helps eliminate or reduce wastes, promotes personal growth of employees and the company, provides guidance for employees, and serves as a barometer of leadership. Each Kaizen may be small, but the cumulative effect is tremendous.
Benefits
Quick and easy Kaizen empowers employees, enriches the work experience and brings out the best in every person. It improves quality, safety, cost structures, delivery, environments, throughput and customer service.
The Process
The Quick and Easy Kaizen process works as follows:
- The employee identifies a problem, waste, or an opportunity for improvement and writes it down.
- The employee develops an improvement idea and discusses it with his or her supervisor.
- The supervisor reviews the idea within 24 hours and encourages immediate action.
- The employee implements the idea. If a larger improvement idea is approved, the employee should take leadership to implement the idea.
- The idea is written up on a simple form in less than three minutes.
- Supervisor posts the form to share with and stimulate others and recognizes the accomplishment.
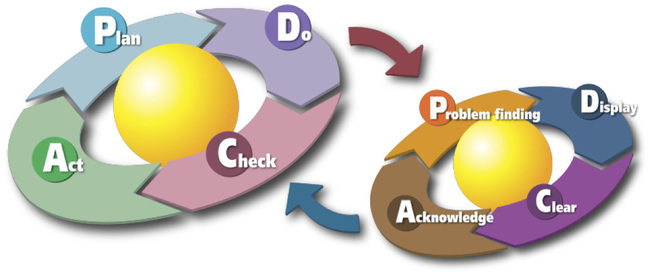
Three Key Characteristics
- Permanent method changes. Change the method. Once the change is made, you can’t go back to the old way of doing things.
- Continuous flow of small ideas. The smaller ideas, the better. Kaizen is small ideas. Innovation takes time and is costly to implement, but kaizen is just day-to-day small improvements that when added together represent both enormous savings for the company and enormous self-esteem for the worker.
- Immediate local implementation. Be realistic. Kaizen is done within realist or practical constraints.
Source of Information: Japan Human Relations Association
The Japan Human Relations Association (JHRA) is leading the quick and easy kaizen efforts throughout Japan with its training programs, workshops, and publications. JHRA only promotes quick and easy kaizen. They dropped all of the other HR functions for they believe that quick and easy kaizen is the best way to develop human resources within a company.
After WWII, to help restore Japan, American occupation forces brought in American experts to help with the rebuilding of Japanese industry. The Civil Communications Section (CCS) developed a Management Training Program that taught statistical control methods as part of the overall material. This course was developed and taught by Homer Sarasohn and Charles Protzman in 1949-50. Sarasohn recommended W. Edwards Deming for further training in Statistical Methods.
The Economic and Scientific Section (ESS) group was also tasked with improving Japanese management skills and Edgar McVoy was instrumental in bringing Lowell Mellen to Japan to properly install the Training Within Industry (TWI) programs in 1951.
Prior to the arrival of Mellen in 1951, the ESS group had a training film to introduce the three TWI "J" programs (Job Instruction, Job Methods and Job Relations)---the film was titled "Improvement in 4 Steps" (Kaizen eno Yon Dankai). Thus the original introduction of "Kaizen" to Japan. For the pioneering, introduction, and implementation of Kaizen in Japan, the Emperor of Japan awarded the 2nd Order Medal of the Sacred Treasure to Dr. Deming in 1960. Consequently, the Union of Japanese Science and Engineering (JUSE) instituted the annual Deming Prizes for achievement in quality and dependability of products.
On October 18, 1989, JUSE awarded the Deming Prize to Florida Power & Light Co. (FPL), based in the US, for its exceptional accomplishments in process and quality control management. FPL was the first company outside Japan to win the Deming Prize.
Reference:
- Liker, J. K., & Meier, D. (2006).The Toyota way fieldbook: a practical guide for implementing Toyota's 4Ps. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Japan Human Relations Association
- US National Archives - SCAP collection - PR NewsWire
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed